General characteristics of the forest pathological situation in the forest fund of the Republic of Belarus
At the end of 2018, the focal area in the Republic of Belarus amounted to 152,794 ha, including those requiring control measures of 40,074 ha, which is 53725 and 33519 ha less than in the same period last year, respectively.
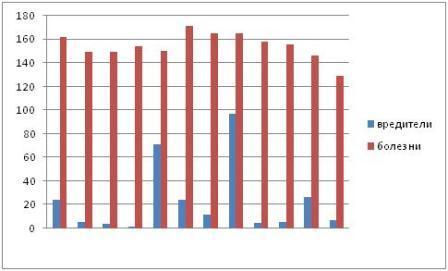
At the end of 2018, in the forest fund of the Forestry Forestry of the Republic of Belarus, foci of pests and forest diseases acted on a total area of 136517 ha, including 32459 ha requiring control measures. Compared to the same period last year, this area decreased by 35976 and 22425 ha, respectively. Forest diseases accounted for 91.6% of all foci in the Republic of Belarus and 94.6% for MHF RB, of which foci of the root sponge account for about 68%.
The dynamics of foci of pests and forest diseases according to the MLF RB:
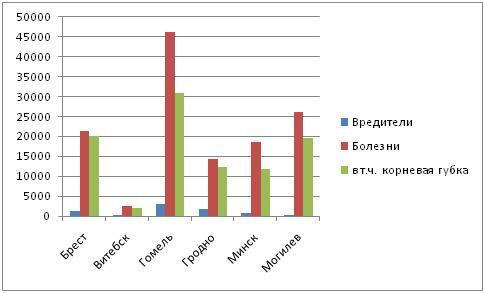
As in previous years, the largest areas of foci of pests are concentrated in the forest plantations of the Gomel State Forestry Enterprise, where their share is 36.2% of the total area of foci in the MLF of the Republic of Belarus and 32.3% in the Republic of Belarus, the smallest (2.1% in the MLF Belarus and 1.9% in the Republic of Belarus) – in the stands of the Vitebsk GPLHO.
Of the pine-eating pests in 2019, the most dangerous will be an ordinary pine sawfly of 1024 hectares and a pine silkworm of 648 hectares, including those requiring control measures of 75 hectares. In addition, in January 2019, the Bellesozashchita Institution along the border of the pine silkworm center in the Solonsky forestry GLHU Zhlobin Forestry revealed a new pine silkworm center in the Krasnoberezhsky forestry on an area of 299 hectares, including those requiring control measures of 105 hectares
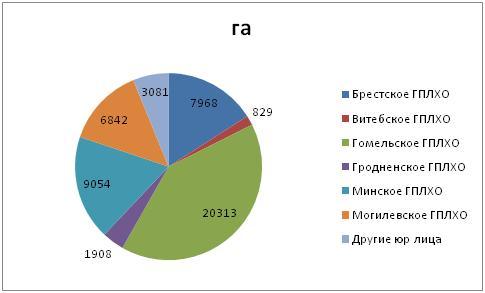
In the forest fund of the Republic of Belarus, under the influence of various adverse factors of an abiotic and biotic nature, he died in 2018. 49 995 ha of plantations, which is 1.4 times more than in 2017, while coniferous plantations (99%) were mainly affected by the death. The maximum loss of forest stands in 2018 was recorded on the territory of the Gomel GPLHO – 20313 ha, or 40.6% of the total area of dead plantations in the Republic of Belarus.
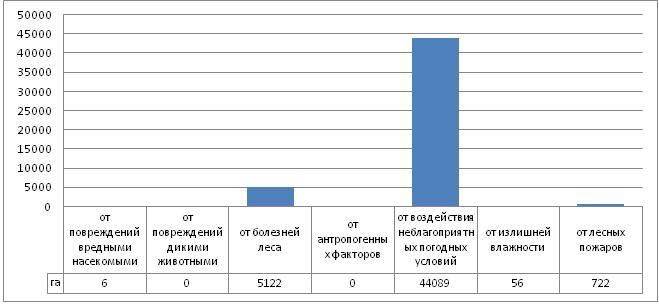
In 2018, the prevailing factors that caused catastrophic consequences were adverse weather conditions, from which 92.7% of the stands died, respectively. The main cause of adverse weather conditions was the formation of a windfall and windbreak under the influence of strong squally winds.
Compared to the previous year, the growth of plantations from forest fires increased 4.0 times, 2.2 times from diseases, 1.3 times from exposure to adverse weather conditions, and the loss of plantations from excessive humidity decreased 1.2 times. From damage by harmful insects killed 6 hectares.
Pine plantations
The forest pathological and sanitary state of the republic’s pine forests in 2018 was determined by a set of adverse environmental factors: hurricane winds, droughts, forest fires and others, which led to weakening of plantings and a decrease in their resistance to plants and biocidal against pathogens.
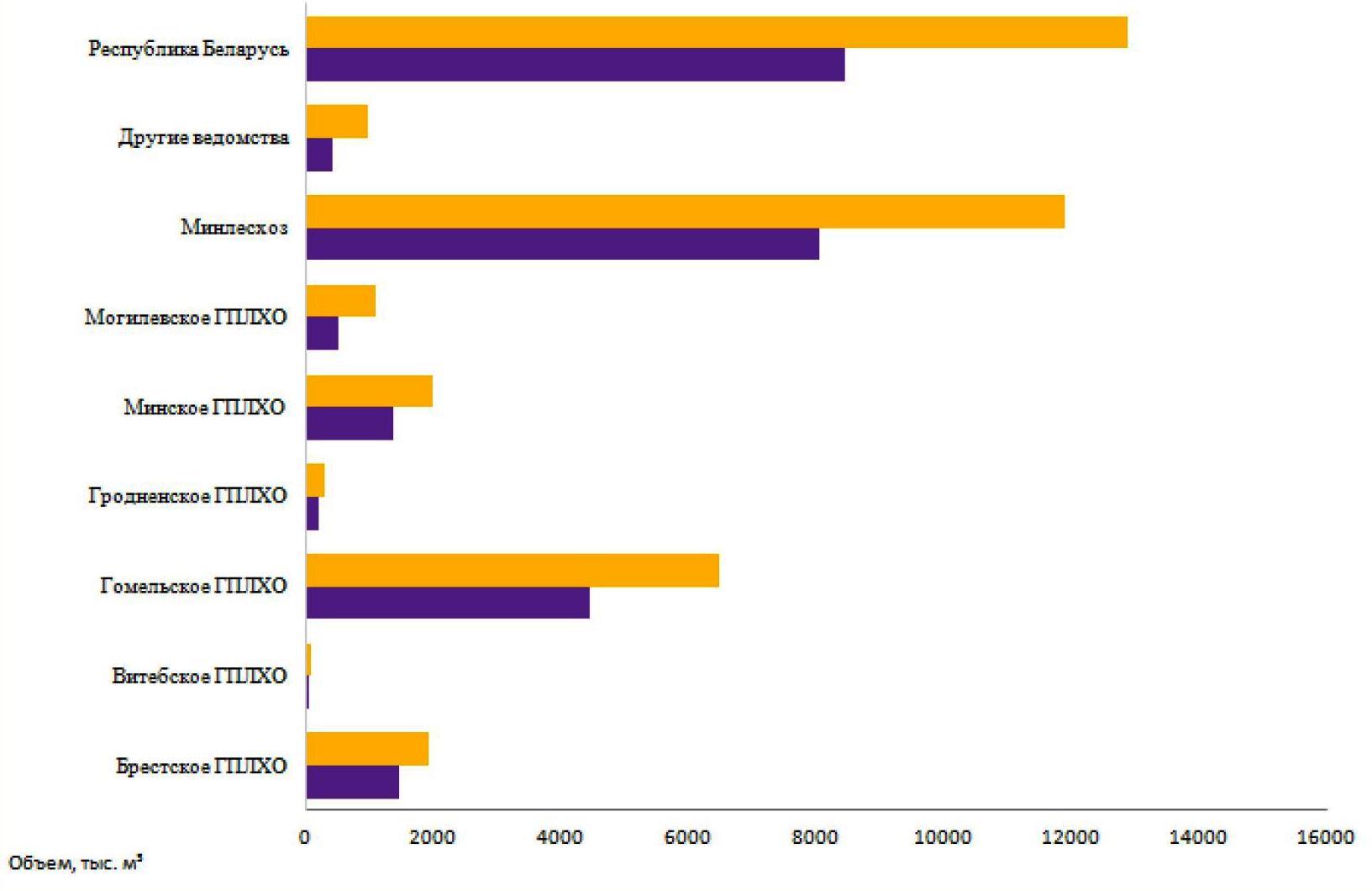
In 2018, the area and stock of drying pine plantations requiring sanitary and recreational measures exceeded the level of 2017 by 1.5 times and in the whole country amounted to 208035 ha and 12860.6 thousand m3. The largest volumes of damaged pine forests were concentrated in the leskhozes of Gomel (6463.52 thousand m3), Minsk (1997.27 thousand m3) and Brest (1940.66 thousand m3) GPLHO, and their largest excess compared to 2017 was noted in Vitebsk (2.2 times), Mogilev (2.2 times) GPLHO and in other departments – 2.4 times.
In the forestries of the Ministry of Forestry, the area of damaged pine plantations amounted to 194,366.0 ha with a stock of 11,880.28 thousand m3. Conducting full sanitary felling in the Ministry of Forestry was required on an area of 39687.0 ha with a reserve of 10219.62 thousand m3, selective sanitary felling – 74 831.0 ha (924.78 thousand m3), cleaning of litter – 79848.0 ha (735.88 thousand m3). Sanitary and health measures were carried out on 97.1% of the required area.
Geography of clear felling in pine stands for 2018:
Spruce stands
According to the results of a monthly survey by the leshozes of the sanitary condition of spruce stands in 2018, it was established that the area of the stands that have lost their biological stability, requiring clear cutting, amounted to 9293 ha with a volume of 3244 thousand m3.
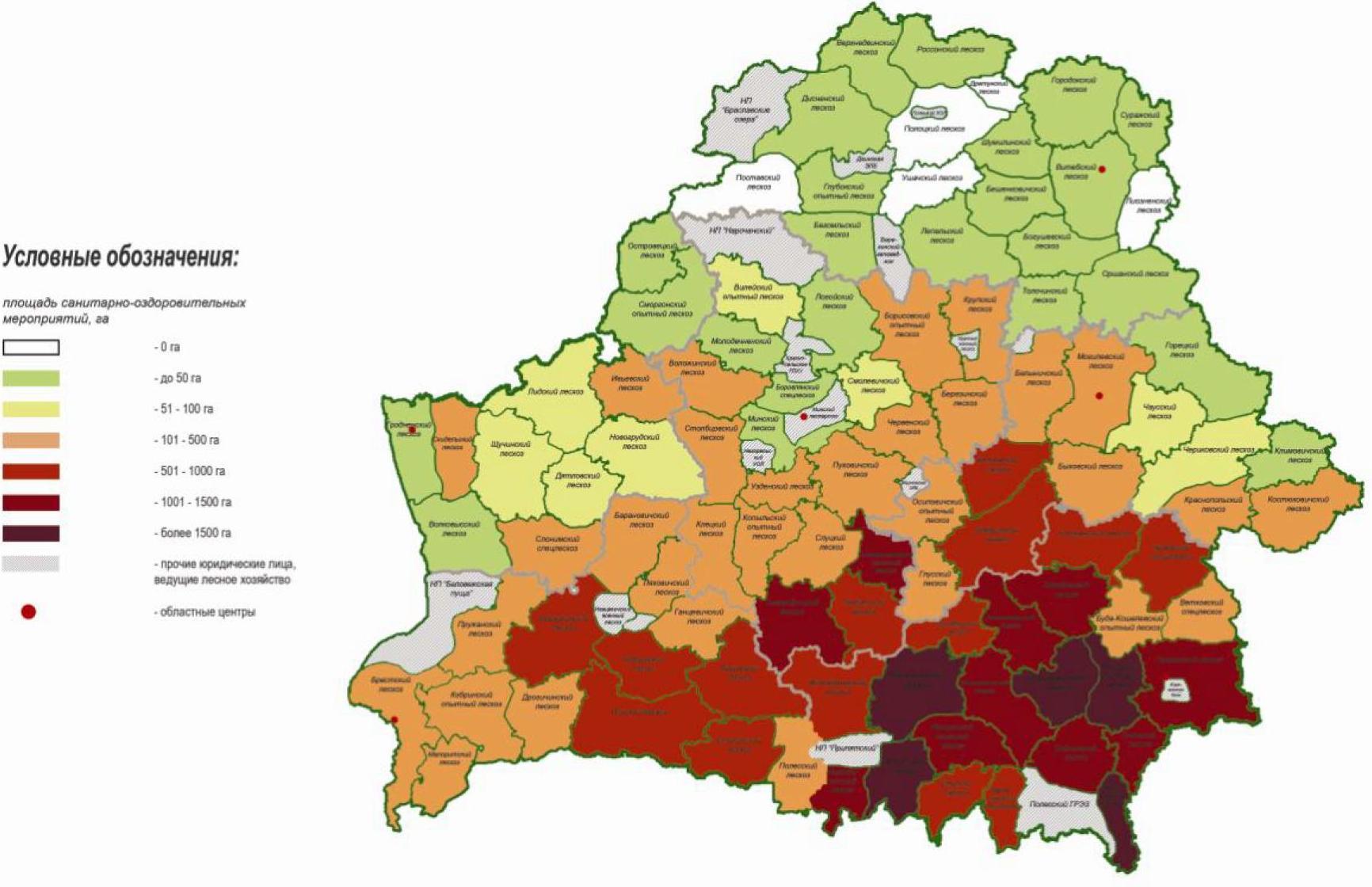
Compared to 2017, the volumes of spruce stands requiring clear cutting, as a whole, increased 1.7 times in the MLC. In the context of the GPLHO, the situation in drying spruce forests is ambiguous: an increase in the volume of spruce stands requiring clear cutting was noted in Brest 3.6 times, Gomel 1.9 times.In 2018, drying of spruce forests was recorded in 79 forestry institutions. The largest volumes (from 100 thousand m3 and more) of drying out of spruce plantations that have lost biological stability are located in the following leshozes: Orshansky (193.8 thousand m3) in the Vitebsk GPLHO; Rogachevsky (187.7 thousand m3) in the Gomel GPLHO; Kopylsky (100.3 thousand m3), Luban (225.0 thousand m3), Starodorozhsky (161.9 thousand m3) in the Minsk GPLHO; Bobruisk (127.2 thousand m3), Bykhovsky (284.8 thousand m3), Goretsky (157.6 thousand m3), Mogilev (217.7 thousand m3) in the Mogilev State Forestry Complex and accounted for 53.3% of the total according to the MLC of the volume of spruce trees that have lost biological stability. The distribution of drying volumes of spruce plantations across the territory of the republic is presented in Figure 3.3.
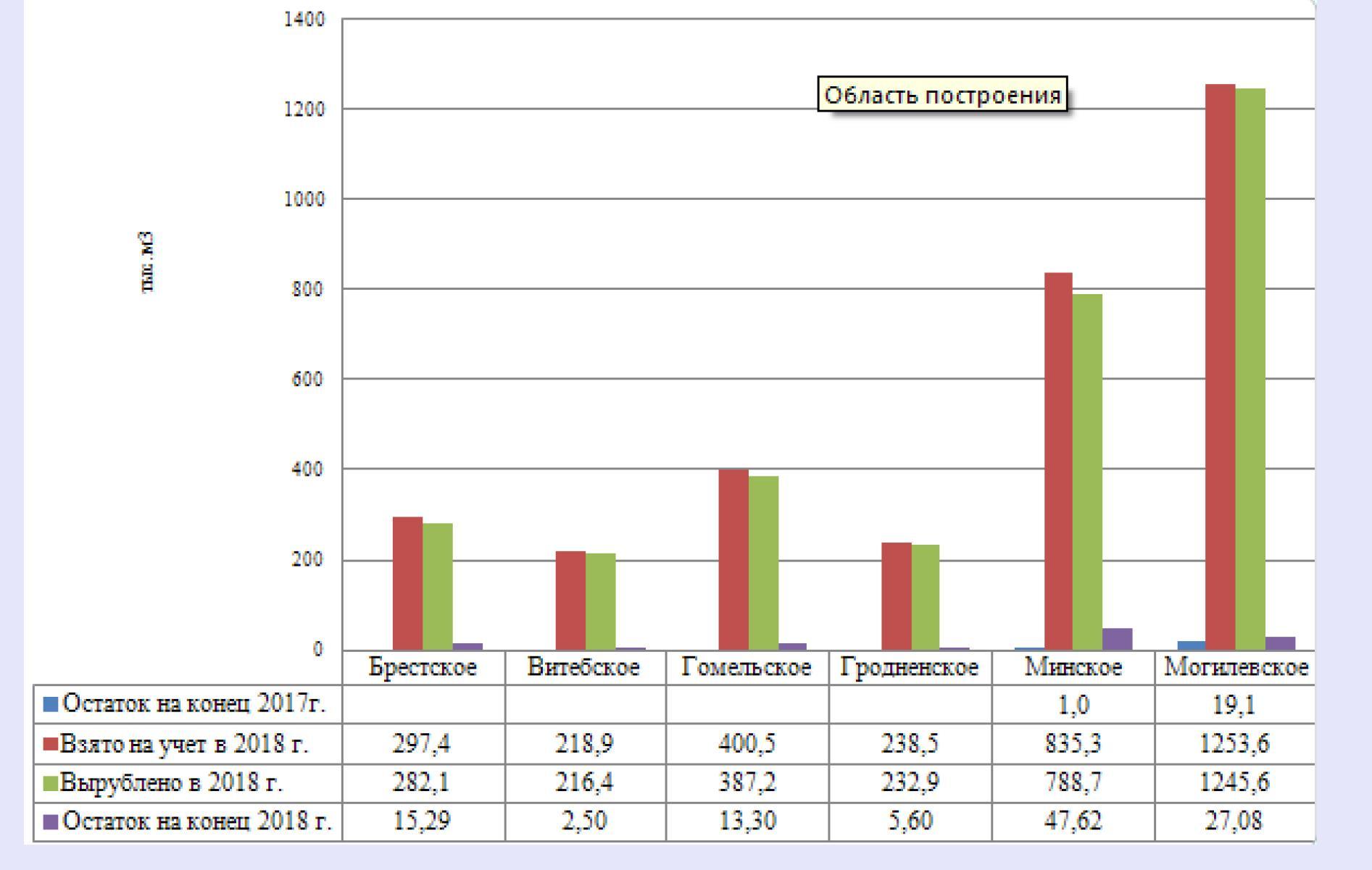
In 2018, 8042.9 hectares with a volume of 140.31 thousand m3 of spruce forests of the second class of biological sustainability requiring selective sanitary felling, including those on the State Forestry and Forest Trade Plan, were registered: Brest – 1048.8 hectares with a volume of 14.82 thousand. m3, Vitebsk – 2443.3 hectares with a volume of 45.09 thousand m3, Gomel – 36.2 hectares with a volume of 0.61 thousand m3, Grodno – 664.1 hectares with a volume of 17.02 thousand m3, Minsk – 1838 , 3 hectares with a volume of 34.48 thousand m3, Mogilev GPLHO – 2012.2 hectares with a volume of 28.19 thousand m3.
Compared to 2017, the volume of spruce stands requiring selective sanitary felling in the Ministry of Forestry remained at last year’s level, including in the Vitebsk and Grodno GPLHO. An increase in the volumes of spruce stands requiring selective sanitary felling took place in the Brest GPLHO – 2.1 times and in the Minsk GPLHO – 1.3 times; a decrease in the volumes of spruce stands requiring selective sanitary felling was noted in Gomel – 1.4 times, Mogilev – 1.7 times.
In order to reduce the food supply of stem pests, reduce their number, as well as minimize damage and stabilize the condition of spruce stands, a set of measures was taken in 2018 to protect spruce stands, including: examination of spruce stands, registration of identified foci of stem pests; pheromone surveillance of the bark beetle by the typographer; detailed monitoring of the sanitary condition of spruce stands on permanent plots; clear felling; selective sanitary felling; laying wood hunters; protection of harvested wood.
Analyzing the data of pheromone surveillance conducted in 78 leshozes for the first and second generations of the bark beetle, the following was established: for the first generation of the bark beetle, there was an increase in the number of pests compared to 2017 in all GPLHO except Vitebsk GPLHO, in which the number of pests decreased (table 4.1). Also, in the second generation of the bark beetle, the typographer noted an increase in the number of the pest population in all GPLHO, with the exception of the Brest GPLHO, in which a decrease in the number of pests was recorded.
The maximum number in the first generation of the bark beetle of the printing house was recorded in Telekhansky (Lesser Plotnitsky forestry – 9030 units), Orsha (Orsha forestry – 5500 units), Zhlobinsky (Lugovirnyansky forestry – 17326 units), Schuchinsky (Zheludok forestry – 29700 units). ), The Starodorozhsky experimental (Gorkovsky forestry – 22612 units) and Bykhovsky (Novo-Boyarsky forestry – 31768 units) leshozes.
The maximum abundance for the second generation of the pest was recorded in Ivatsevichsky (Bronno-Gorsky forestry – 3200 pcs.), Orsha (Orsha forestry – 2900 pcs.), Zhlobinsky (Lugovirnyanskoye forestry – 17326 pcs.), Schuchinsky (Schuchinskoe forestry – 4800 pcs.) , Borovlyansky special forestry (Ratomsk forestry – 12490 pcs.), Bobruisk (Bobruisk forestry – 25650 pcs.) Forestries.
Considering the above facts, the high survival rate of the bark beetle in the winter, as well as the favorable climatic conditions for the flight of the bark beetle, the drying of spruce plantations in 2019 will continue with an increase in volumes.
Oak plantations
The main factors determining the forest pathological and sanitary state of oak plantations in recent years were: leaf-eating pests, root rot caused by openings, vascular and necro-cancerous diseases.
Leaf-eating pests
At the beginning of 2017, the area of foci of the winter moth amounted to 1,192.7 ha, including 2.5 hectares requiring control measures; during the year, pest outbreaks arose on an area of 473.9 ha. During 2017, it died out under the influence of natural factors of foci of the winter moth on an area of 1012.6 ha. At the end of the year, the area of foci of the winter moth was 654 ha. The maximum number of winter moths was recorded in Baranavichy (Gorodishche forestry – 65 pcs.), Liozno (Zalessky forestry – 151 pcs.), Mozyr experimental (Sloboda forestry – 205 pcs.), Dyatlovsky (Leonovichsky forestry – 83 pcs.), Borisovsky ( Neman forestry – 16 pcs.), Bobruisk (Domanovo forestry – 58 pcs.) Leshozes.
In order to monitor the abundance of the winter moth and green oak leaflet, as well as to monitor their dynamics in oak stands, pheromone dispensers “OWABEN” and “TORVABAT” were used. The drug “OWABEN” was used on an area of 35,475 ha.
Pheromone monitoring of the green oak leaflet in 2017 was carried out on an area of 7950 ha. The maximum number of pests was recorded in Liozno (73 pcs.), Vitebsk (68 pcs.), Ushachi (22 pcs.), Berezinsky (18 pcs.) Kostyukovichi (17 pcs.) Leshozes.
Forest diseases
At the beginning of 2017, the area of foci of vascular mycosis of oak forests amounted to 314.7 ha, including 314.7 ha requiring control measures. In 2017, foci of oak vascular mycosis were identified in Gomel (17 ha), Zhitkovichi (2.8 ha) and Khoiniki (2.9 ha) forestries on a total area of 22.7 ha. At the end of the year, the area of foci of vascular mycosis was 314.7 hectares, including 314.7 hectares requiring control measures.
The foci of the oak sponge, as well as transverse oak cancer, remained unchanged during 2017 and amounted to 6.9 hectares (Klimovichi forestry) and 3 hectares (Shumilinsky forestry), respectively. Other diseases of oak plantations in 2017 were identified on an area of 20.8 hectares. During the year, foci of oak diseases were eliminated as a result of forest protection measures on an area of 83.8 ha, and died out under the influence of natural factors of foci of diseases on an area of 18.5 ha. At the end of the year, the area of foci of oak diseases amounted to 4494.2 hectares, including 1915.2 hectares requiring control measures.
Ashen plantings
Over the past two decades, in extremely dry growing periods, characterized by significant deficit of precipitation, high temperature and low humidity of the atmospheric air, ash plants have been drying out in the Republic of Belarus.
Over the past decade (2006-2016), there has been a significant decrease in the area of ash plantations. The death processes of ash trees are most pronounced in the Brest GPLHO, where the total area of plantations decreased by 45.6%, in the Mogilev GPLHO – by 36.9%, Vitebsk – by 35.3%, Minsk – by 27%, Gomel – by 20, 6%, Grodno – by 9.7%.
The main biotic factors that negatively affect the state of ash plantations in 2017, as well as for the entire observation period, were: root and stem rot.
At the beginning of 2017, the area of foci of diseases operating in ash plantations amounted to 1244.4 ha. Sanitary and health measures during the year were carried out on an area of 157.3 hectares. At the end of the year, the area of foci of diseases amounted to 1119.4 ha, including 111 ha requiring control measures. Compared with 2016, there was a decrease in the area of foci of ash diseases by 10%.
Foci of root rot of ash, as newly emerging during 2017, were recorded on an area of 112.5 hectares, including 78.0 hectares in the Vitebsk GPLHO, 29.9 hectares in Gomel and 4.6 hectares in Grodno.
During 2017, 341.6 hectares with a cut-off stock of 6.6 thousand m3 of ash plantations with impaired biological stability, requiring selective sanitary felling, including the State Forestry and Chemical-Chemical Combine: Brestskoye – 65.8 hectares with a margin of 0.29, were taken into account. thousand m3, Vitebsk – 128.7 hectares with a reserve of 3.55 thousand m3, Gomel – 29.9 hectares with a reserve of 1.01 thousand m3, Grodno – 29.5 hectares with a reserve of 0.33 thousand m3, Minsk – 71.1 ha with a reserve of 1.35 thousand m3; Mogilevskoye – 16.6 ha with a reserve of 0.11 thousand m3. Selective sanitary cuttings in ash plantations by forestry institutions were not carried out in full. The undeveloped residue of damaged ash plantations amounted to 16.7 hectares with a reserve of 0.7 thousand m3 (Gorodoksky forestry – 16.1 hectares, Ivievsky forestry – 0.6 hectares). The largest volumes of desiccant ash plantations requiring sanitary-improving measures were recorded in Gorodok, Stolin and Starobinsky forestries.
In the reporting year, employees of the Bellesozashchita Institution conducted a reconnaissance forest pathological examination of ash plantations in Disnensky, Vitebsk, Yelsky, Mozyr and Starobinsky forestries.
According to the results of the survey, root rot is found in 40-68% of trees, trunk and branch cancer is found in 50-62% of ash trees, water shoots were observed in 70-88% of trees.
According to the results of the examination of the ash trees of the foci of stem pests of the great Hylesinus crenatus F. and the variegated ash-tree beetles Hylesinus fraxini Panz., As well as damage to the ash emerald narrow-body goldfish Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire were not found.
Birch plantations
In July-August 2017, there were favorable weather conditions for the development of bacterial dropsy on hardwood.
In 2017, the area of newly emerged foci of this disease in birch stands amounted to 62.7 hectares in the forest forestry area (Gomel GPLHO Gomel forestry 12.2 hectares, Zhitkovichi forestry 1.2 hectares, Zhlobin forestry 1.2 hectares, Mozyr forestry 2.8 hectares, Khoiniki forestry 15.3 ha and Minsk GPLHO Borisov forestry 9 ha, Luban forestry 7 ha, Chervensky 14 ha). The area of foci eliminated or extinct as a result of forest protection measures is 91.3 ha. At the end of 2017, according to the MLC, the area of the foci of bacterial dropsy was 449.1 ha, including 391.2 ha requiring control measures.
In 2017, foci of stem pests of birch plantations arose in the Minsk GPLHO Luban forestry on an area of 1 hectare, but liquidated or extinct as a result of forest protection measures.
Foci of stem rot (white marble-like core-sapwood rot) in birch plantations in 2017 were identified on a total area of 9 hectares, including in the Borisov forestry on an area of 8 hectares, in the Molodechno forestry on an area of 1.0 hectares. Sanitary and health measures were taken in these stands.
For comparison, in 2016, according to the MLC, the area of foci of bacterial dropsy in birch stands was 477.7 ha, including 418.8 ha requiring control measures.
Forest crops and young growths
In 2017, pests and diseases of this ecological group damaged mainly coniferous plantings.
As of the beginning of 2017, shootout centers operated on a total area of 277.1 hectares in the Kobrin, Polesky, Stolin forestries of the Brest GPLHO, Vasilevichi, Kalinkovichi, Rechitsa, Svetlogorsk forestries of the Gomel GPLHO, Bobruisk forestry of the Mogilev GPLO. Under the influence of natural factors, the pest foci died out in the Brest GPLHO (1 ha). At the end of 2017, runaway foci remained active in all the above forestry institutions, on a total area of 281.1 hectares. All of them do not require control measures.
At the beginning of 2017, the centers of pine weevil operated on a total area of 304.1 ha. In 2017, foci re-emerged on an area of 41 hectares; 50 ha of pest outbreaks were eliminated as a result of forest protection measures.
The largest number of pests arose: in the Polessky leskhoz (29 ha) of the Brest GPLHO, 216.1 ha of damaged territory died out under the influence of natural factors over the past year, Polessky (95 ha), Lelchitsky (4 ha), Tolochinsky (5 ha), Zhlobinsky ( 40.4 ha), Khoiniki (80.7 ha), Klimovichi (2 ha) and Kostyukovichi (77 ha) leshozes; at the beginning of 2018, the area of existing outbreaks was 79 ha.
At the beginning of 2017, the area of foci of an ordinary spruce sawfly was 450.9 hectares, including 22.9 hectares requiring measures. During the past year, 245.9 ha of foci of an ordinary spruce sawfly died out under the influence of natural factors. At the end of 2017, the pest settlement area was 222.0 hectares, which do not require control measures.
The area of foci of khrushchas operating at the end of 2017 is 75.6 hectares, which are located in Ivatsevichi (1 ha), Polessky (18 ha), Stolin (6 ha) leshozes of the Brest GPLHO, Vitebsk (1 ha) leshoz of the Vitebsk GPLHO, Yelsky ( 2.3 ha), Kalinkovichi (18.1 ha), Komarinsky (1.8 ha), Milosevic (0.3 ha), Mozyr (4.9 ha), Narovlyansky (2.1 ha), leskhozes of the Gomel GPLHO, Luban (1 ha), Minsk (1 ha) forestry enterprises of the Minsk GPLHO, Bobruisk (18.1 ha) and Chausky (1.0 ha) forestries of the Mogilev GPLHO. Of these, control measures for 1 hectare are required: in Ivatsevichi, Vitebsk, Luban, Minsk and Chaussky forestries.
In the Verkhnedvinsk and Lepel forestries, the aphid center was eliminated on an area of 5 ha.
In Polesskoye (1 ha) and Stolin (1 ha) forestries, the existing foci at the end of 2017 were a single sawfly-weaver on a total area of 4 hectares.
As of the beginning of 2017, foci of a pine sub-root bug were operating on a total area of 72.5 hectares in Ivatsevichi (3 hectares), Kobrinsky (7 hectares) leshozes of the Brest GPLHO, Grodno leshoz (21 ha) of the Grodno GPLHO, Glussky leshoz (41.5 ha) Mogilev GPLHO. Under the influence of natural factors, the pest foci died out in the Rossonsky forestry (12 ha). Foci again appeared in the Ivatsevichi forestry (3 ha). The foci of a pine-headed horse bug in Brest GPLHO (10 ha), Grodno GPLHO (21 ha), Mogilev GPLHO (41.5 ha) remained active. 3 ha control measures are required in the Ivatsevichi leskhoz.
The foci remained to operate: yellow Germes – 3 ha in the Liozno Forestry of the Vitebsk GPLHO, ordinary shyutte pine in the Stolbtsovsky Forestry of the Minsk GPLHO on an area of 5 ha, pine vertun – 24 ha in the Minsk GPLHO in Starodorozhsky (4 ha) and Stolbtskhoz (20 ha).
The area of the foci of diplodiosis operating at the beginning of 2017 was 26.3 ha; during the year, foci were identified on an area of 16.4 ha, in Baranavichy (6 ha), Logoisk (9 ha), Minsk (9 ha) and Belynichi (1.4 ha) leshozes. Forest protection measures were carried out on an area of 1.4 ha, pruning of the affected branches with their subsequent burning, and also died out under the influence of natural factors – 1.3 ha. At the end of the year, foci remained on the area of 40.0 ha.